- Home
- Research
- Spectroscopy and Imaging
- Work-Groups
- Molecular Imaging
Molecular Imaging
The Molecular Imaging group investigates new chemically sensitive linear and non-linear spectroscopic contrast mechanisms, laser technologies and detection methods for multi-contrast and multi-parameter imaging of biological and biomedical target structures (e.g. tissue samples (thin sections, 3D samples, organs), biological cells, marker molecules (e.g. drugs)) and innovative materials (e.g. self-healing polymers). The application focus is on molecular and functional diagnostics in medicine and the life sciences as well as material characterization. In addition, the Molecular Imaging working group focuses on the integration of the researched multimodal approaches into compact, clinically usable automated systems with a high TRL level for preclinical and prospective clinical studies. The clinical focus is on tumor diseases and infectious diseases, as these diseases have a high medical need in terms of early diagnosis and therapy.
Research Topics
- Automated non-linear multimodal CARS/SRS/SHG/TPEF/FLIM imaging for morphochemical tissue characterization
- Multimodal (CARS, SRS, SHG, TPEF, FLIM) microscopy and intravital microscopy for (I) label-free visualization of biomolecules (lipids, proteins, endogenous chromophores/autofluorophores such as NAD(P)H and FAD, elastin, as well as SHG-active macromolecules such as collagen etc.), (II) for targeted observation of the localization of active ingredients and their release dynamics, (III) for the visualization of small Raman labels (alkyne tags, stable isotope labels) in cells, tissue and organs and (IV) for the characterization of intelligent materials.
- Research into in vivo suitable multimodal non-linear (CARS, SRS, SHG, TPEF) spectroscopic probe concepts (imaging fibers, rigid endoscopes with gradient index lenses, transport fibers)
- Research into new concepts for high-resolution (coherent) Raman microscopy
- Establishment of new non-linear contrast mechanisms in multimodal imaging approaches
- Realization of microfluidic sampling concepts for nonlinear multimodal imaging
- Implementation of concepts for combined laser-based therapy and diagnostics (fs-laser ablation and multimodal imaging)
- Research into fiber laser concepts for fast spectral tuning with extremely low noise (RIN), high robustness and compact design especially for clinical applications
Innovative multimodal molecular imaging approaches with a focus on non-linear contrast phenomena are being researched with the aim of imaging biomolecules in cells, tissues and organs. In addition to the realization of compact setups for clinical use, the technological research focus is on the optimization and improvement of central parameters such as: spatial and spectral resolution, acquisition speed, spectral bandwidth of detection, sensitivity (single photon counting method), molecular specificity or penetration depth.
Areas of application

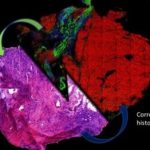
- Medical pathological diagnostics: spectral histopathology ex vivo and in vivo
- Oncology: tumor diagnostics and therapy
- Infection diagnostics
- Cytometry
- Mechanisms of action of drugs
- Live cell microscopy
- Therapy monitoring
- Characterization of intelligent materials
The application-oriented focus of the non-linear multimodal imaging approaches being researched is on improved disease diagnostics and tailored therapy as well as new insights into dynamic life processes and the molecular understanding of intelligent materials. Furthermore, new fields of application for molecular imaging are constantly being developed in close cooperation with physicians, life scientists and material scientists.